Note: Proofread any scripts before using. Always try scripts on a test instance first. This Blog is not responsible for any damage.
Oracle Automatic Storage Management - Concepts
- Oracle ASM is a volume manager and a file system for Oracle database files.
- It supports single-instance and Oracle RAC configurations.
- Oracle ASM also supports a general purpose file system that can store application files and oracle database binaries.
- It provides an alternative to conventional volume managers, file systems and raw devices.
- Oracle ASM distributes I/O load across all available resource to optimize performance.
- In this way, it removes the need for manual I/O tuning (spreading out the database files avoids hotspots).
- Oracle ASM allows the DBA to define a pool of storage (disk groups).
- The Oracle kernel manages the file naming and placement of the database files on the storage pool.
| Disk groups |
- Oracle ASM store data files on disk groups.
- A disk group is a collection of disks managed as a unit by Oracle ASM.
- Oracle ASM disks can be defined on:
- A disk partition: Entire disk or a section of disk that does not include the partition table (or it will be overwritten).
- A Disk from a storage array (RAID): RAID present disks as Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs).
- A logical volume.
- A Network-attached file (NFS): Including files provided through Oracle Direct NFS (dNFS).Whole disks, partitions and LUNs can also be mounted by ASM through NFS.
- Load balance: Oracle ASM spreads the files proportionally across all of the disks in the disk group, so the disks within a disk group should be in different physical drives.
After you add a disk, Oracle ASM performs rebalancing.
Data is redistributed to ensure that every file is evenly spread across all of the disks.
- Disks can be added or removed from a disk group while the database is accessing files on that disk group (without downtime).
- Oracle ASM redistributes contents automatically
- Oracle ASM uses Oracle Managed Files (OMF).
|  |
| Mirroring and Failure groups |
- Disk groups can be configured with varying redundancy levels.
- For each disk in a disk group, you need to specify a failure group to which the disk will belong.
- A failure group is a subset of the disks in a disk group, which could fail at the same time because they share hardware
- Failure groups are used to store mirror copies of data.
- In a normal redundancy file, Oracle ASM allocates a primary copy and a secondary copy in disks belonging to different failure groups.
- Each copy is on a disk in a different failure group so that the simultaneous failure of all disks in a failure group does not result in data loss.
- A normal redundancy disk group must contain at least two failure groups.
- Splitting the various disks in a disk group across failure groups allows Oracle ASM to implment file mirroring.
- Oracle ASM implements mirroring by allocating file and file copies to different failure groups.
- If you do not explicitly identify failure groups, Oracle allocates each disk in a disk group to its own failure group.
Oracle ASM implements one of three redundancy levels:
|  |
 |
(a) Diskgr1 below implements 2-way mirroring. Each disk ( dasm-d1, dasm-d2) is assigned to its own failure group.SQL> Create diskgroup diskgr1 NORMAL redundancy
2 FAILGROUP controller1 DISK
4 '/devices/diska1' NAME dasm-d1,
3 FAILGROUP controller2 DISK
5 '/devices/diskb1' NAME dasm-d2
6 ATTRIBUTE 'au_size'='4M';
|  |
|  |
| Oracle ASM Instance |
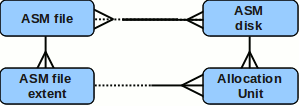
Oracle ASM metadata:
|
- With Oracle ASM an ASM instance besides the database instance needs to be configured on the server.
- An Oracle ASM instance has an SGA and background processes, but is usually much smaller than a database instance.
- It has minimal (how much?) performance effect on a server.
- Oracle ASM Instances are responsible for mounting the disk groups so that ASM files are available for DB instances.
- Oracle ASM instances DO NOT mount databases.
- They only manage the metadata of the disk group and provide file layout information to the database instances.

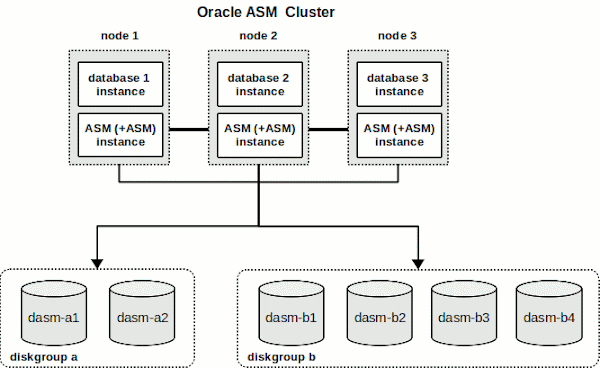
ASM Instance on Clusetered configurations:
- One Oracle ASM instance in each cluster node.
- All database instances in a node share the same ASM instance
- In a Oracle RAC environment, the ASM and database instances on the surviving nodes automatically recover from an ASM Instance failure on a node.